Axial Fan Optimization Using TCFD and CAESES
CFD Support and FRIENDSHIP SYSTEMS jointly worked on an efficient and automated design workflow to optimize the rotor blades of an axial fan. The motivation and starting point of this work was the fact that fan designers and fan manufacturers often have good baseline designs of axial fans that they want to further optimize and improve.
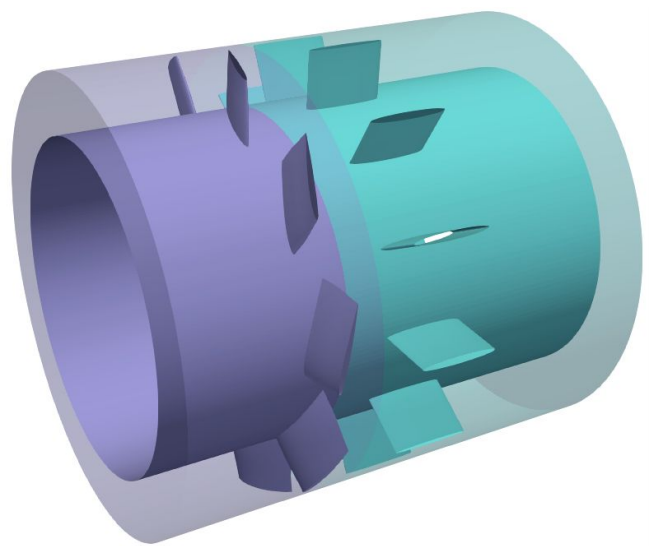
Starting point for many fan manufacturers: An initial axial fan geometry which should be further optimized
Typical objectives for the engineering of fan components are as follows:
- Maximize the fan efficiency while considering certain flow rates
- Increase the air flow capacity
In the presented case study, the baseline fan specifications were:
- Diameter = 280 mm
- RPM = 3000
- Initial Power Rating = 100 W
- Max Pressure = 410 Pa
- Max Air Capacity = 1100 m3 / h
- Peak Efficiency = 69%
Flexible Geometry Model for Automated Studies
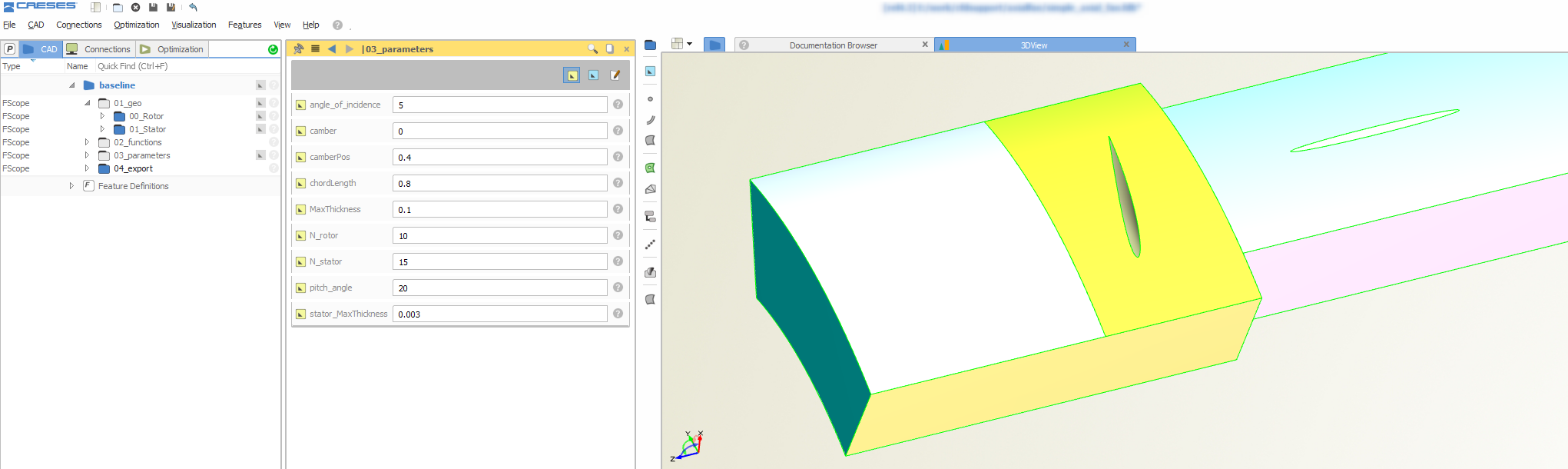
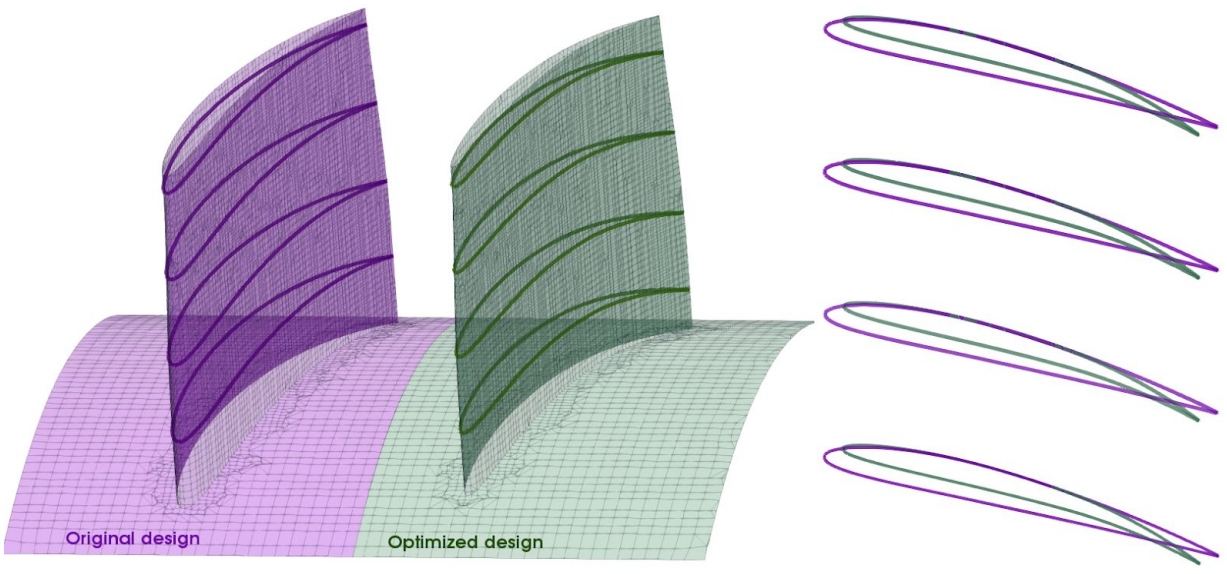
Based on the initial geometry which was provided in a standard CAD format, FRIENDSHIP SYSTEMS set up a fully-parametric fan model in CAESES. The goal of this new geometry model was to have the relevant design parameters available (e.g. camber and thickness control, chord length etc.) while also being able to fully automate the geometry generation. Each new design candidate should be analyzed by CFD (Computation Fluid Dynamics) for which a parametric periodic flow volume was also automatically generated in CAESES. The stator blade was also parametric variable geometry, but it remained fixed for this study.
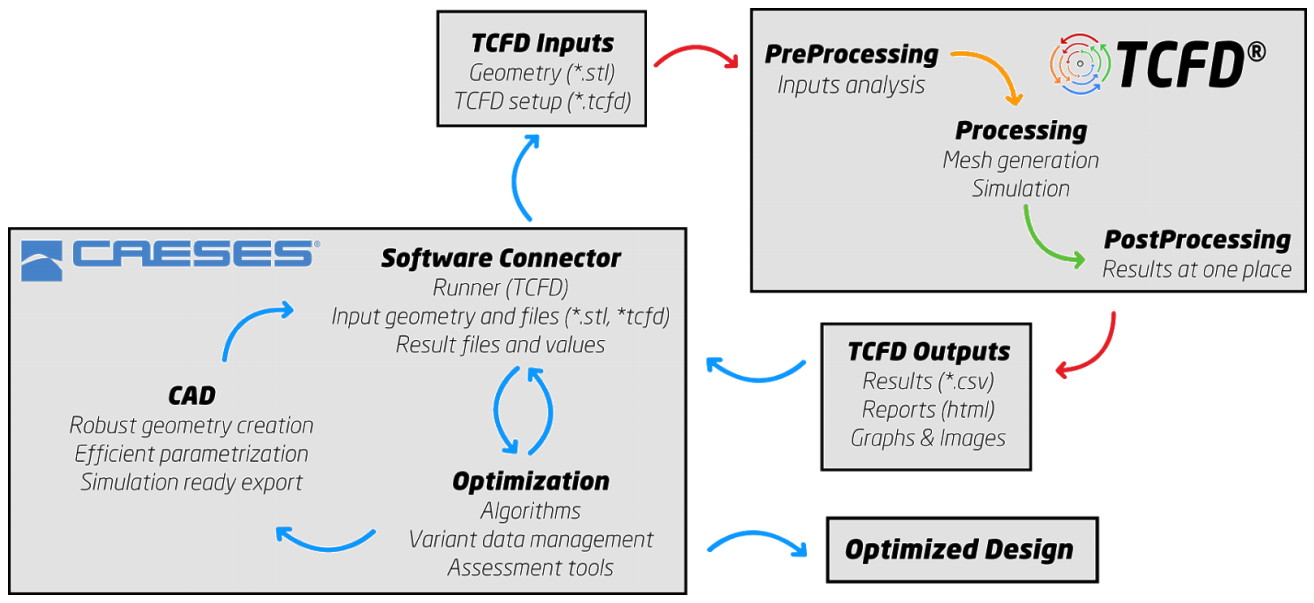
CFD Setup and Automation
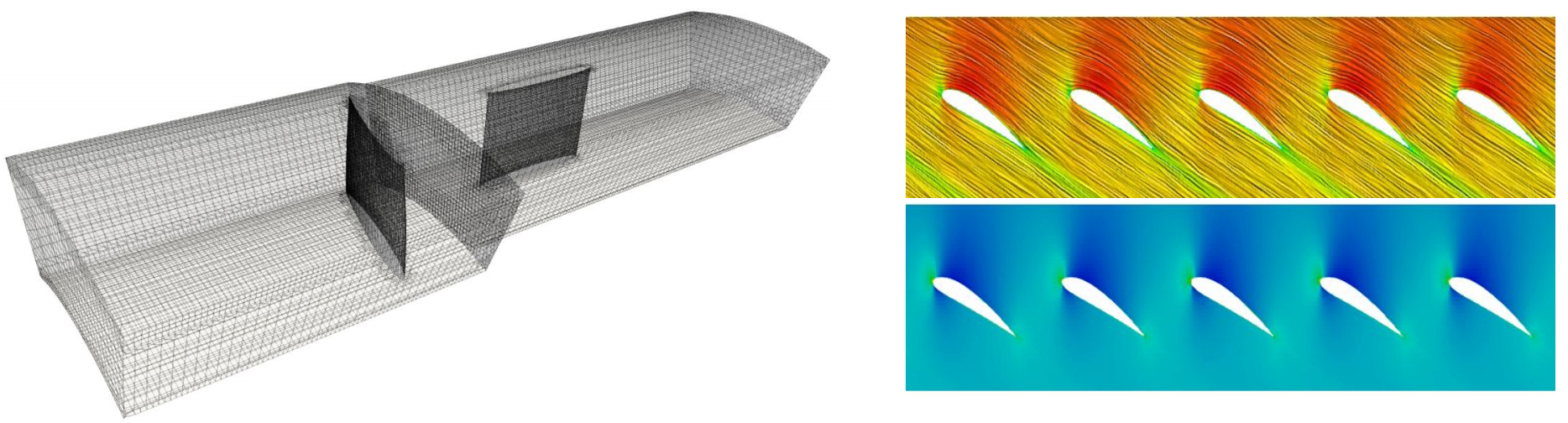
In a next step, TCFD was coupled to CAESES and entirely automated, so that a new design candidate could be created and analyzed with a single click. Mesh generation and CFD analysis were set up once for the baseline design and reused without manual interaction for all generated designs.
Optimization Process
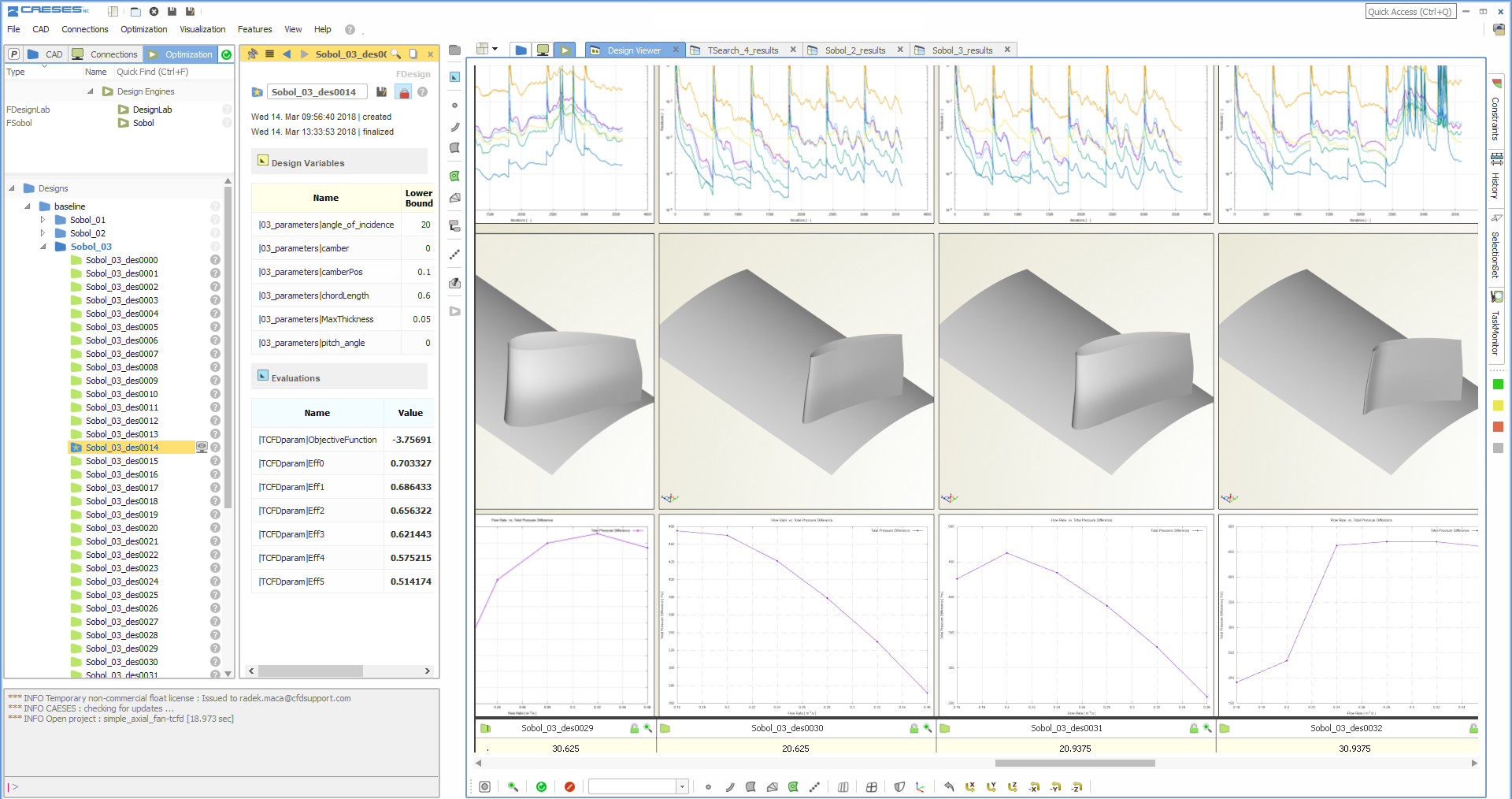
For the automated optimization process, the integrated DoE and optimization strategies of CAESES were used. For a first exploration and sensitivity analysis, 250 designs were created using a pseudo-random sampling method. In a next step, relevant design variables were selected and a local optimization was conducted for a few promising design candidates.
Optimization Results
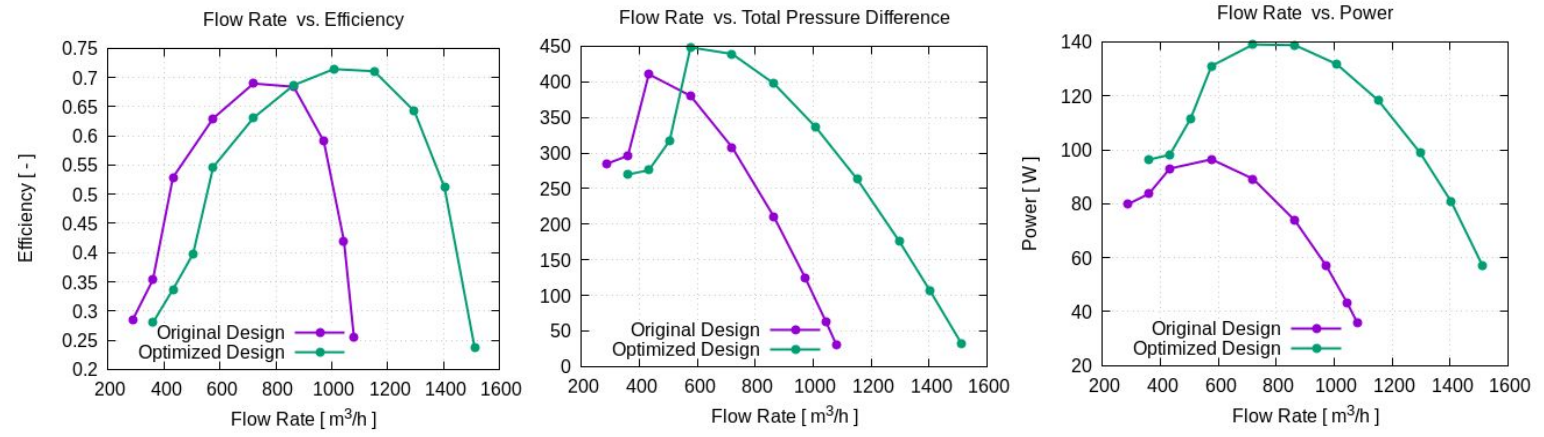
The total computational time spent on this study was roughly 900 CPU hours, and the optimization was carried out within 3 days (over the weekend). The final optimized design had a maximum air capacity of more than 1500 m3/h, while the peak efficiency was increased from 69% to 72%. The maximum pressure rose to 450 Pa and the working range was also wider. The price of these significant improvements was an additional 40 W in power requirement.
Download Case Study
There is a PDF file that summarizes the case study with a few additional pictures and some more details.
More Information
If you are interested in CFD-driven shape optimization, check out the CAESES turbomachinery section.
There is also a blog post about axial fan noise reduction.