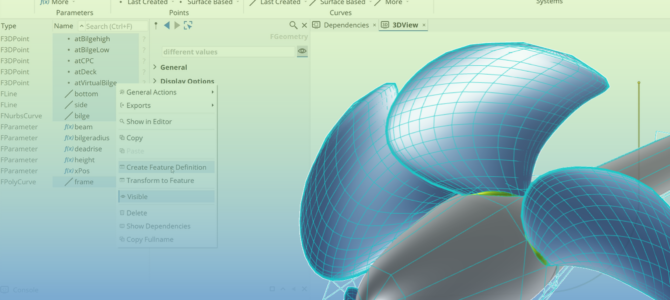
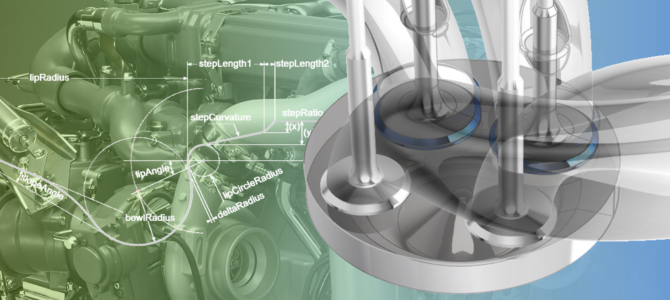
Engineering teams often struggle with fragile parametric models, complex design spaces, and costly redesign loops. In this blog, we highlight five key challenges in modern engineering workflows and show how a robust, optimization-ready approach with CAESES helps teams design more efficiently and make better data-driven decisions.