FRIENDSHIP SYSTEMS has released version 4.1 of its upfront modeling and optimization software CAESES® and CAESES® Free. All details about new features, changes and bug fixes can be found in our changes log.
Geometry Kernel and Triangulation
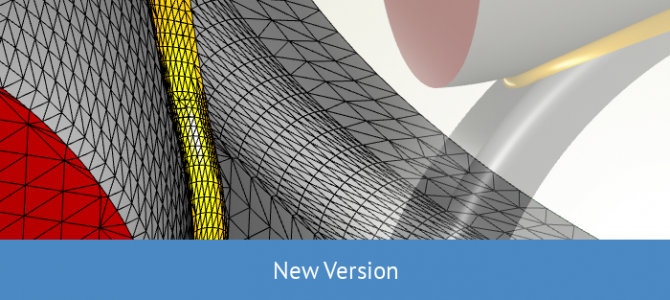
With version 4.1, we have a lot of great improvements in our geometry kernel. Many geometry operations have been made robust for difficult modeling tasks. In addition, the surface triangulation which is important for STL exports has been completely reviewed as well.
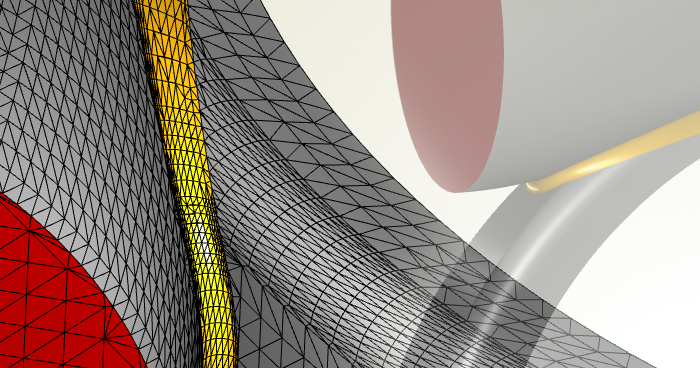
Improved surface triangulation for generating closed STLs
New Export Format for Robust Automation
This is a highlight that has been on our list for a long time: The tetin (*.tin) file export for a tighter connection with ANSYS ICEM CFD. For automated processes our users had issues with using ICEM CFD in an automated process. Previously, when you imported a CAESES® model into ICEM CFD using IGES or similar formats, the IDs of edges and faces were mixed up and not unique anymore. Our users needed to implement inconvenient workarounds to realize a robust automated workflow. With the new *.tin export, the unique CAESES® IDs of edges and faces are directly transferred to ICEM CFD, and the user can rely on them when setting up a meshing process. This is now 100% robust for automation, for both structured and unstructured meshes. So here is a big thanks to our users for pushing and requesting this feature!
As a side note, we had another request from our users to offer a DXF export. As a result, version 4.1 now supports a reasonable subset of this format, which is typically used to export 2D information for drawings within traditional CAD systems.
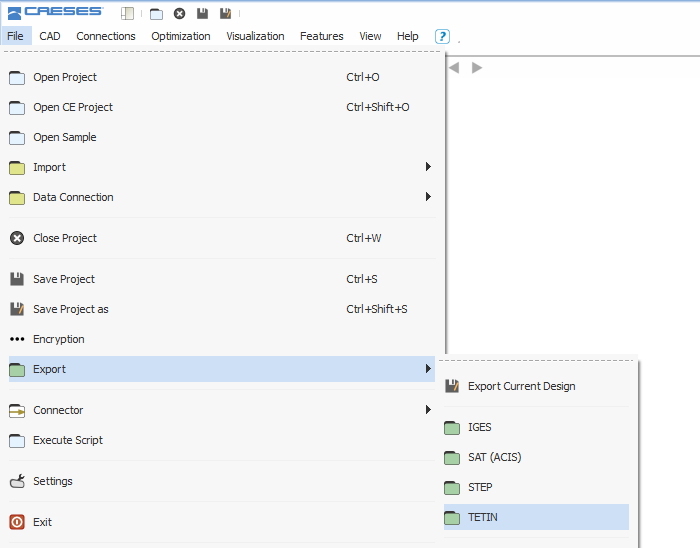
Support for the Tetin- and the DXF-format
Better Surface Representations
We fixed several bugs that had rather large impacts on the overall performance of CAESES®. But not only the performance is better now, we have also improved internal geometry representations: Perhaps you have not been aware of this detail so far, but previously the sweep surfaces approximated the involved curve sections. This had technical reasons and was based on our former geometry structures. With version 4.1, we avoid approximations in the sweep transformation and for the sweep surface, so that the surface representations are made of the exact curve sections.
Shift Transformations
For surface shift transformations, the user can now control the approximation quality through the image surface. This speeds up the entire process of applying shape changes, e.g. for deforming ship hull geometries. Another option that we have added is the possibility to transform the underlying NURBS representation (i.e. the control points, without rebuilding the surface). This has tremendous effects on the performance of such a transformation and is sufficient for most situations.
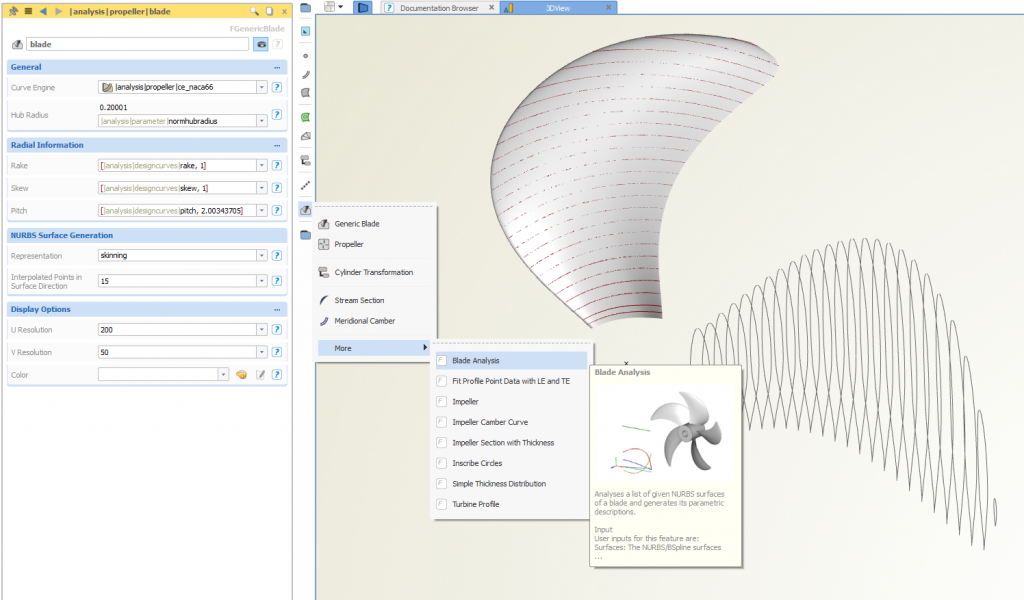
Blade Analysis
We also improved our blade analysis routine for converting a “dead” propeller geometry into a smart parametric model, check this post for more details.
Update of Dakota Version
For users of our add-on advanced optimization, we updated the Dakota toolkit to the latest version 6.3 and reviewed the pre-configured methods. There is also a new template for readily using a single-objective genetic algorithm.
Once again, here is our changes log for more details. We recommend all our users to download and install this new version. We look forward to receiving your feedback!